Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month continues on! However let’s face it, awareness by itself is not enough! To have an impact, we need to take action against colon cancer. We must also have the necessary tools, tactics, and training to take care of business when polyps rear their ugly head. It's a bad month to be a polyp!!!
Now there is a new product called Eleview (Aries Pharmaceuticals) that is specifically made for endoscopic procedures requiring submucosal injection. This product is supplied in 10-mL ampules and is ready-to-use, making it much faster and more convenient to just ask for in the middle of a procedure
Why wouldn't a fellow endoscopist sent their patients for a procedure that is as effective, safer, with no significant recovery time, and far less expensive when compared to surgery?
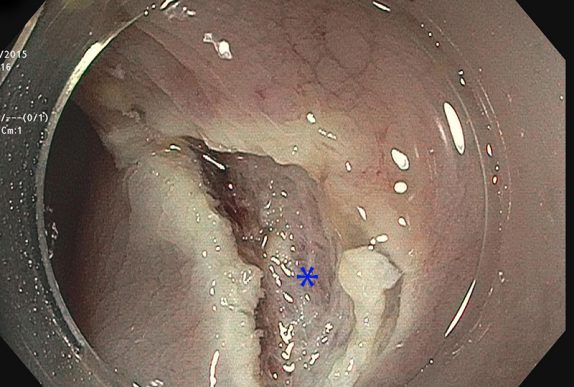
After removing a large polyp endoscopically, it is recommended to follow up the site about 3-6 months later to make sure the entire lesion was removed and prove there is no further adenomatous tissue to resect.
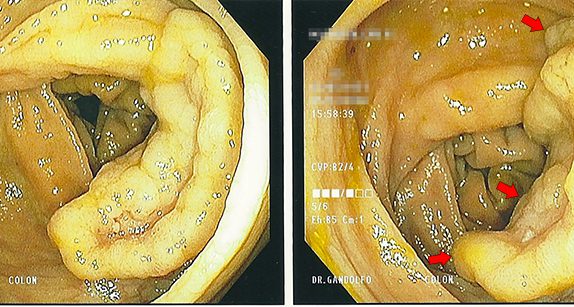
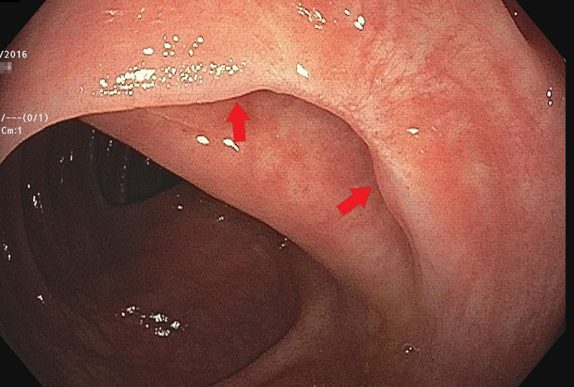
Sometimes repositioning the lesion is what it takes to get it done. A better angle between the snare and the polyp can be the difference between sliding over the top or capturing the lesion. In this case, retroflexing the scope in the ascending colon was the key maneuver needed to get the rest of the polyp out.
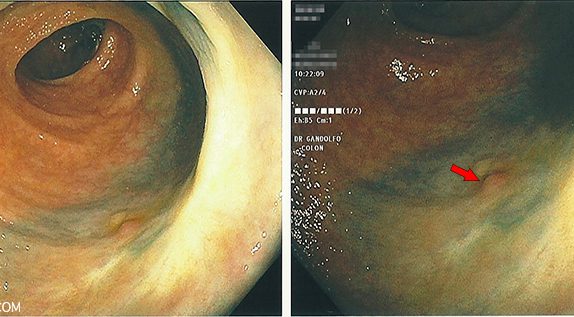
Three month follow up after removal of a small colon tumor with colonoscopy. Did the resection work, or did the patient ultimately need surgery?
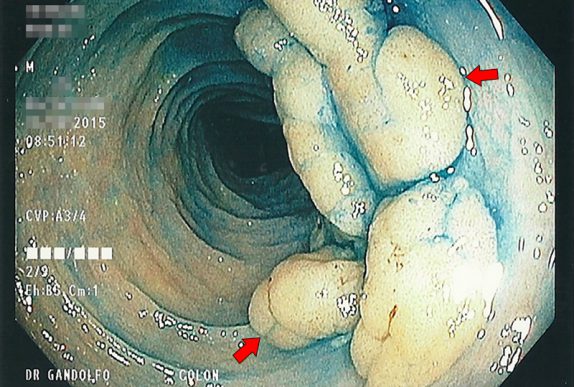
Knowing your limits is a very important part of doctoring. As Mark Twain said, "Good decisions come from experience. Experience comes from making bad decisions." Tackling big polyps with the scope is no exception to this rule. Although techniques for removing large polyps have evolved over the years, and maneuvers that were once deemed "high-risk" are now being taught fairly routinely to junior GI fellows, there is still an individual comfort level that practitioners should identify in themselves and respect.
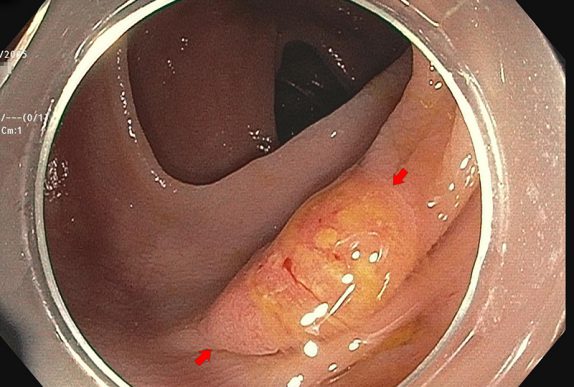
I was surprised when the pathologist called me a few days later about the patient, since pathologists usually only call when a result is malignant or unusual. This "polyp" which I estimated to be about 15-mm in greatest diameter was a serrated adenoma (not a surprise) but also contained an 8-mm focus of adenocarcinoma. Luckily, the carcinoma portion of the polyp was completely resected with clear margins on all sides, however this polyp was truly an early-stage colon cancer!
This lesion exhibits the "mucus cap" sign. There is a thick layer of mucus adherent to the polyp that remains attached even after washing with the water jet on the scope. The mucus cap sign is often seen with a particular type of polyp called a serrated polyp. These are often located in the right side of the colon, and are thought to be easier to miss on colonoscopy due to the flat nature of their growth. Unfortunately, they can still transform into colon cancer.
Many lesions that have been deemed "not endoscopically resectable" can actually be safely removed by a gastroenterologist with training and experience in EMR.